Indonesia enters 2025 with a steady 5% growth rate, strong trade surplus, and growing global influence as part of the BRIIC bloc. With a $1.4 trillion economy powered by natural resources, manufacturing, and a rapidly expanding middle class, the country continues to balance stability with transformation. This report breaks down the latest data, trade patterns, and policy trends shaping Indonesia’s economy, offering a clear look at where the nation is headed in the year ahead.
Table of Facts and Figures
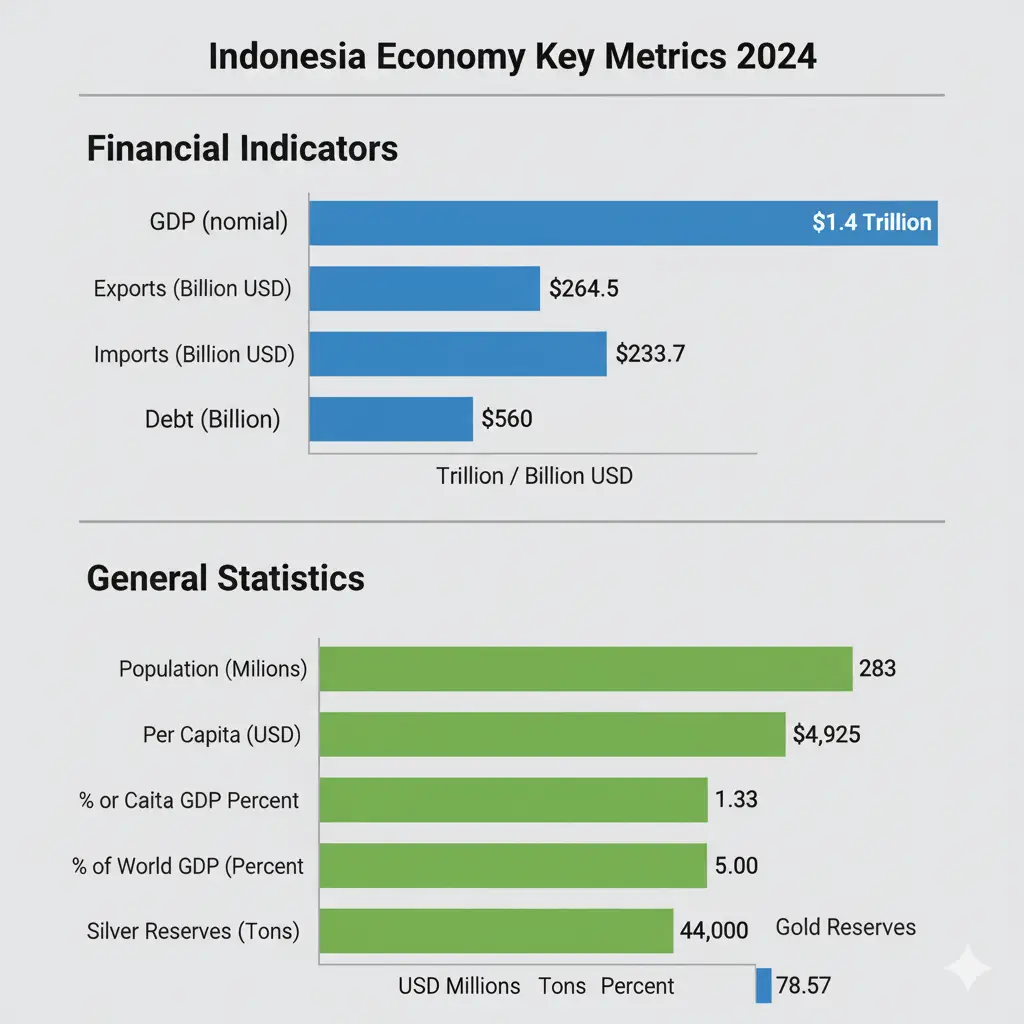
To grasp the pulse of the Indonesia economy, let’s examine core metrics from 2024. These figures reveal a nation balancing expansion with stability, positioning it strongly for Indonesia economy 2025. Below is a table summarizing vital stats, followed by remarks on each term to explain their implications.
| Indicator | Value 2024 | Remarks |
| GDP | $1.4 T (nominal) | Represents total economic output; this marks a solid base, contributing to Indonesia economy ranking as the 16th largest globally by nominal terms. High commodity reliance boosts resilience against shocks. |
| Growth | 5.00% | Annual real GDP increase; this rate outpaces many peers, signaling Indonesia economy growth driven by manufacturing and services, with projections holding steady into 2025. |
| Population | 283 million | Total residents; a young demographic (median age ~30) fuels labor supply, supporting consumption-led expansion in the Indonesia economy. Urban migration accelerates this trend. |
| Per Capita | $4,925 | GDP divided by population; reflects average income, up from prior years, aiding middle-class rise key to what type of economy does Indonesia have—a mixed model blending market and state elements. |
| % of World GDP | 1.33% | Share of global output; underscores how big is Indonesia economy, especially in PPP terms (~3.4% at $4.1T), enhancing its voice in forums like G20. |
| Imports | $233.7 B | Value of goods/services bought abroad; covers energy needs, with rises tied to industrial growth in Indonesia economy updates1. |
| Exports | $264.5 B | Value of goods/services sold abroad; surplus strengthens reserves, central to why is Indonesia economy growing via commodities. |
| Debt | $560 B | Total government borrowing; at ~39% of GDP, it’s manageable, allowing fiscal room for infrastructure without straining Indonesia economy news. Low ratios reassure investors. |
| Gold Reserves | 78.57 Tons | Central bank holdings; acts as a hedge against volatility, bolstering confidence in what is the economy of Indonesia amid currency fluctuations. |
| Silver Reserves | 44,000 Tons | Mineral stockpiles; supports the mining sector, a pillar of exports, with potential for value addition in Indonesia economy type—resource-rich emerging market. |
These indicators paint a picture of stability. For instance, the 5% growth rate exceeds the global average, thanks to policies promoting digital and green sectors. Compare this to broader trends via our world economy ranking 2025 guide.
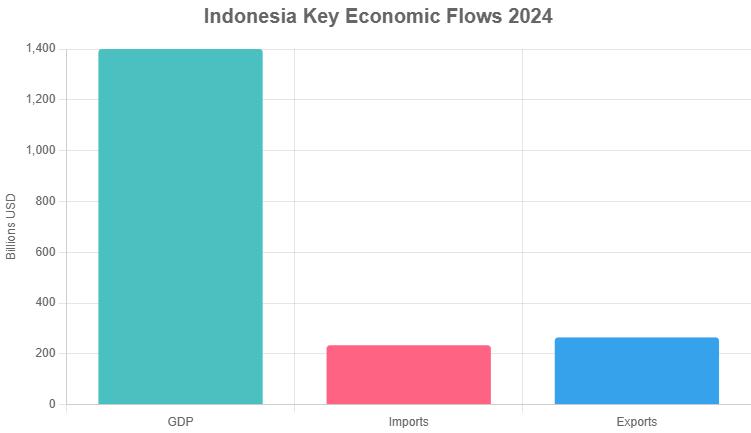
Here’s a quick bar chart visualizing the scale of GDP, imports, and exports in billions of USD—note how exports edge out imports, signaling a healthy trade balance.
Major Imports and Exports Shaping the Indonesia Economy
Trade remains the engine of the Indonesia economy, with exports often outpacing imports to build forex reserves. In 2024, the country exported $264.5 billion worth of goods, focusing on natural resources that align with global demand for sustainable energy.
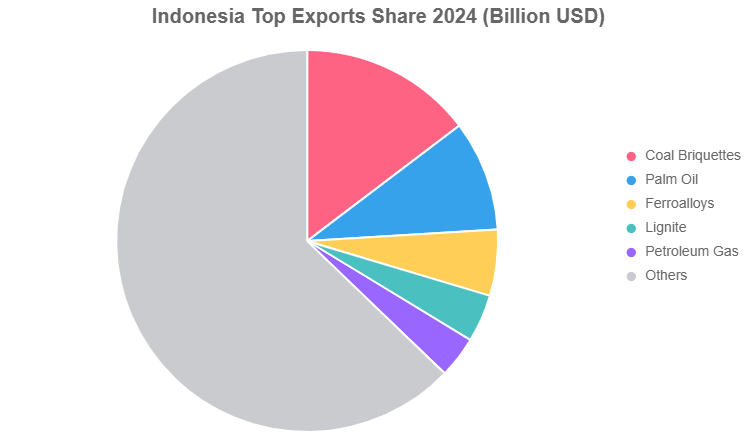
Top Exports
- Coal Briquettes: $38.8B – Power energy transitions worldwide; key to Indonesia economy growth 2025.
- Palm Oil: $24.8B – Dominant in food and biofuels; faces sustainability scrutiny but drives rural jobs.
- Ferroalloys: $14.8B – Essential for steel production; ties into infrastructure booms abroad.
- Lignite: $10.7B – Fuels power plants; highlights what is Indonesia economy based on—extractives.
- Petroleum Gas: $9.3B – Supports LNG exports, a bright spot in Indonesia economy news August 2025.
These exports underscore what kind of economy is Indonesia, a resource exporter evolving toward diversification.
Major Imports
Imports hit $233.7 billion, emphasizing energy security and tech upgrades:
- Processed Petroleum Oils: ~$20B – Refines domestic needs; vulnerable to oil price swings.
- Crude Oil: ~$15B – Fills production gaps in how is the economy in Indonesia.
- Smartphones: ~$10B – Boosts digital adoption amid rising middle-class spending.
- Electronic Circuits: ~$8B – Fuels manufacturing hubs like Batam.
- Wheat: ~$3B – Supports food security for 283 million people.
A trade surplus of ~$31B reinforces stability. For context on global patterns, check our global GDP analysis.
To illustrate export diversity, view this pie chart showing the share of top categories in total exports.
Indonesia Economy News Today: October 2025 Highlights
Staying current with Indonesia economy news today is crucial, especially in October 2025. Central bank actions dominate headlines: Bank Indonesia paused rate cuts on October 24 to push banks on lower loan rates, aiming to spur lending without inflation risks. This reassures markets amid global uncertainties.
Political shifts under President Prabowo add layers, with Indonesia economy news noting economic anxiety from policy tweaks, yet digital resistance grows via youth-led campaigns. On a positive note, the creative economy surged, exporting $12.9B—49% of targets—highlighting soft power in Indonesia economy updates.
Earlier in Indonesia economy news may 2025, growth hit 5.1% in Q2, beating forecasts. Indonesia economy news april 2025 covered EV battery investments, while Indonesia economy news september 2025 focused on deficit stability at 2.78% of GDP. The 2025 Nobel in Economics, awarded for institutions, offers lessons for Indonesia’s knowledge shift—from mines to minds.
These updates affirm Indonesia economy overview 20252: resilient yet adaptive.
The Emerging Role in BRIIC and Global Shifts
The Indonesia economy thrives within BRIIC (Brazil, Russia, India, Indonesia, China)—emerging giants reshaping trade. The current fundamental shift in BRIIC economies has been the growing size and income levels of the middle class. In the space race, China has a sizable world-class technical labor force and high savings and/or investment rates that help contribute to their rising productivity and relatively rapid economic growth. Which concept best describes a world economy in which the engines of growth could comprise several major industrialized and emerging economies, including China, rather than the United States alone? This points to “multipolarity,” where Indonesia economy joins peers like China’s economy and India’s economy as growth poles.
Indonesia’s middle class, now over 50 million, drives consumption, echoing BRIIC trends. Link this to economic globalization for deeper ties. Compared to Brazil’s economy, Indonesia’s lower debt (39% vs. 88% GDP) offers flexibility.
Why is Indonesia economy so bad? It’s not—myths stem from inequality, but how bad is Indonesia economy overlooks 5% growth. Instead, the economy like in Indonesia blends exports with services, asking what economy does Indonesia have? A mixed, developing type with state-guided markets.
Indonesia Economy Outlook 2025: Growth Drivers and Challenges
Looking ahead, Indonesia economy outlook 2025 forecasts 5.1% growth, per IMF3, led by nickel processing and tourism rebound. Indonesia economy growth 2025 hinges on EV supply chains, with exports potentially hitting $280B.
Challenges include climate risks to palm oil and rupiah volatility, but policies like downstreaming minerals reassure. Indonesia economy overview emphasizes diversification—away from coal toward renewables. For rankings, see world economy.
In summary, the Indonesia economy navigates 2025 with optimism, backed by trade surpluses and policy smarts. What steps can Indonesia take next to sustain this trajectory?
7 FAQs on Indonesia Economy
What type of economy does Indonesia have?
Indonesia runs a mixed economy, combining free-market elements with government intervention in resources. This setup supports steady growth while addressing inequalities through subsidies and infrastructure.
What is the economy of Indonesia?
It’s resource-driven yet diversifying into manufacturing and services, with GDP at $1.4T. Key sectors include mining, agriculture, and tech, making it a G20 standout.
How is Indonesia economy doing?
Thriving with 5% growth in 2024, trade surpluses, and rising investments. Recent news4 shows creative exports booming, though rate pauses aim to fine-tune lending.
Why is Indonesia economy growing?
Commodity booms, foreign direct investment in EVs, and a young workforce fuel it. Middle-class expansion adds domestic demand, outpacing regional averages.
What is Indonesia economy based on?
Primarily natural resources like coal and palm oil, plus manufacturing. Efforts to process raw materials locally boost value, enhancing global competitiveness.
How big is Indonesia economy?
16th largest nominally at $1.4T, 7th in PPP terms (~$4.1T). It claims 1.33% of world GDP, with potential to climb via ASEAN integration.
What kind of economy is Indonesia?
An emerging market economy—capitalist with social welfare nets. It’s upper-middle income, focusing on sustainable development amid demographic dividends.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Indonesia economy will shine in 2025 with 5% growth, strong trade surpluses, and a rising middle class driving BRIIC shifts. Indonesia’s economic outlook 2025 stays positive, fueled by diversification and smart policies despite global challenges. Fresh Indonesia economy news today highlights resilience in creative exports and EV investments. Overall, Indonesia proves how Indonesia’s economy is doing—robust and ready for more gains. What’s your take on its next big move?
References
- Trading Economics: Indonesia Indicators – Real-time updates on trade and reserves, helpful for traders. ↩︎
- Wikipedia: Economy of Indonesia – Overview with historical context, great for students. ↩︎
- IMF: Indonesia Profile – Projections and policy insights, ideal for investors tracking emerging markets. ↩︎
- Reuters: Recent News – Timely articles for professionals monitoring volatility. ↩︎