Sweden enters 2025 with cautious optimism after a challenging year of slow growth and high inflation. With a GDP of $610.1 billion in 2024, the economy remains stable but under pressure from global trade shifts and domestic costs. Lower interest rates, wage growth, and strong export performance are expected to lift momentum in the months ahead. As one of Europe’s most innovative and balanced mixed economies, Sweden continues to pair market efficiency with strong social systems—an approach that underpins its resilience and long-term appeal.
Table of Facts and Figures
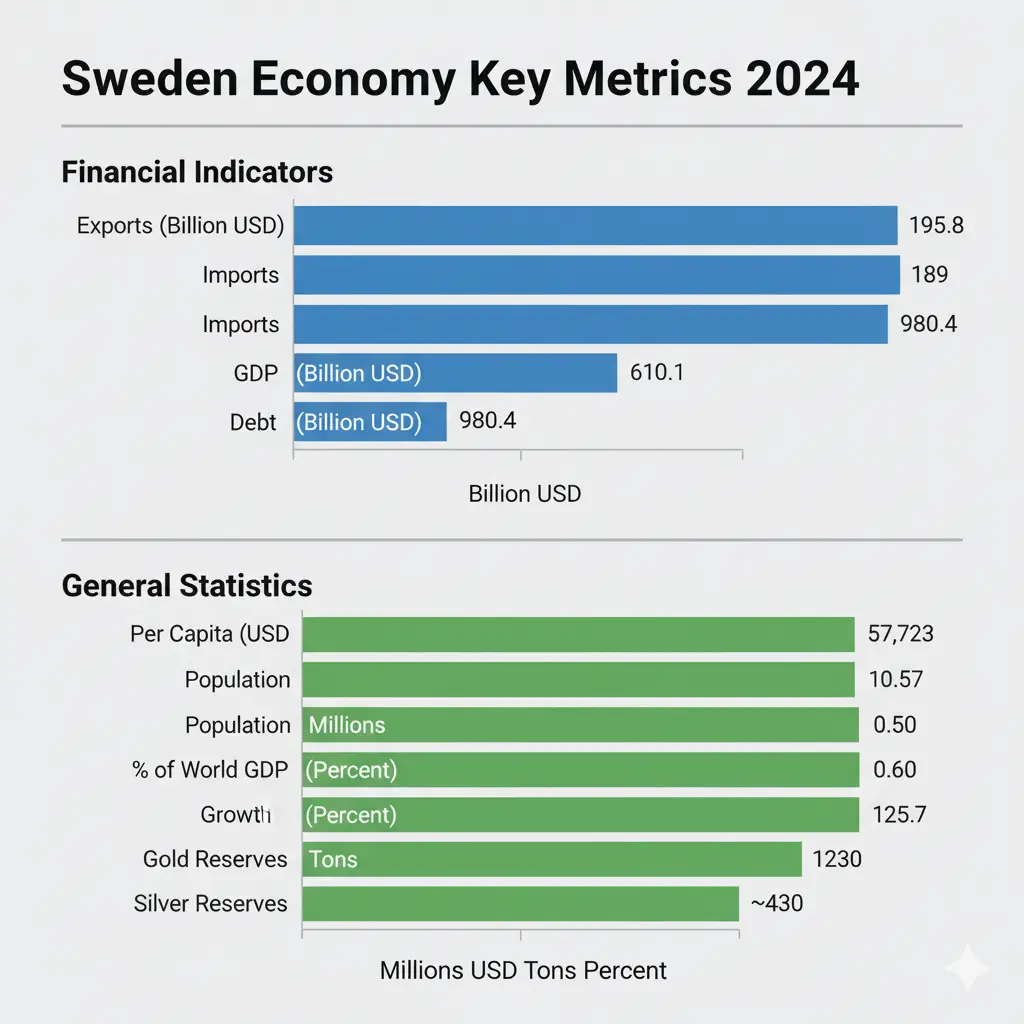
To grasp the pulse of the Sweden economy, let’s examine core metrics from 2024. These figures reveal a nation balancing export strengths against rising debts and sluggish growth. Below is a vertical table summarizing the data, with remarks explaining each term in simple words.
| Metric | Value | Remarks |
| GDP 24 | $610.1 B | Gross Domestic Product measures the total value of all goods and services produced in Sweden over the year. It shows the economy’s1 overall size and health—here, a solid base despite global headwinds. |
| Growth 24 | 0.60% | This is the percentage change in GDP from the prior year. A low 0.60% signals slow expansion, often tied to high inflation and weak demand, but it beats deeper recessions elsewhere. |
| Population – 24 | 10.57 M | Total residents, used to calculate per-person wealth. Sweden’s 10.57 million people enjoy high living standards, supported by strong social safety nets. |
| Per Capita 24 | $57,723 | GDP divided by population, showing average income per person. At $57,723, it highlights Sweden’s affluent status, funding robust public services like free education and healthcare. |
| % of World GDP 24 | 0.55% | Sweden’s share of global output. This 0.55% underscores its role as a small but mighty player in international trade, especially in tech and green energy. |
| Imports 24 | $189 B | Value of goods bought from abroad, like machinery and oil. High imports fuel industries but can widen trade gaps if exports lag. |
| Exports 24 | $195.8 B | Value of goods sold overseas, such as cars and pharmaceuticals. A slight surplus here boosts confidence, proving Sweden’s export machine hums efficiently. |
| Debt 24 | $980.4 B | Total government borrowing. At this level, it equals about 160% of GDP—high but manageable due to low interest rates and credible fiscal policies. |
| Gold Reserves 24 | 125.7 Tons | Central bank holdings of gold as a safe asset. These 125.7 tons act like a financial cushion, valued at around $10 billion, signaling stability in uncertain times. |
| Silver Reserves 24 | ~430 Tons (production basis) | Sweden holds minimal central bank silver, focusing instead on mining2 output. In 2024, production hit 430 tons, mainly from mines like Boliden, supporting electronics and green tech sectors. |
These indicators paint a picture of caution turning to optimism. For instance, the slim growth rate ties into broader Sweden economy recession 2025 fears, yet the export edge offers reassurance.
To visualize trade dynamics, here’s a bar chart comparing 2024 imports and exports:
This chart shows a narrow surplus, a positive sign for the Sweden economy overview 2024.
Major Imports and Exports Driving the Sweden Economy
Trade3 forms the backbone of the Sweden economy. In 2024, exports reached $195.8 billion, edging out imports at $189 billion. Key exports include:
- Cars and vehicles: $14.4 billion, led by Volvo and Scania, powering global mobility.
- Refined petroleum: $10 billion, from efficient refineries meeting Europe’s energy needs.
- Packaged medicaments: $9.14 billion, with AstraZeneca at the forefront in biotech innovation.
- Telecom equipment and machinery: Vital for 5G and automation exports.
On the import side, Sweden relies on:
- Electrical and electronic equipment: Top category, fueling tech assembly lines.
- Machinery and boilers: Essential for manufacturing upgrades.
- Vehicles: Complementing domestic production with foreign parts.
- Chemicals and pharmaceuticals: Supporting R&D in health sciences.
These flows highlight Sweden’s integration into global supply chains. Compared to neighbors, this mix gives Sweden an edge in high-value goods, unlike raw material-heavy peers.
Sweden Economy News Today: October 2025 Highlights
Fresh Sweden economy news today paints a mixed canvas. On October 234, reports emerged on Sweden’s fiscal discipline, offering lessons for peers like France amid deficits from rearmament and Ukraine aid. Inflation forecasts ticked up slightly, with CPIF at 1.6% for 2026, per Riksbank updates.
Unemployment dipped to 8.3% in September, a reassuring 0.1% drop, easing Sweden economy updates today concerns. Meanwhile, the green steel push in Boden—spanning 400 soccer fields—draws Nordic builders into a $7 billion bet on sustainable industry. Kiruna’s mineral boom, including silver output, underscores mining’s role in defense and tech.
These snippets from Sweden economy news october 2025 signal stabilization, with policy rates holding at 1.75% to spur activity. For broader context, see world economy trends.
Sweden Economy 2025 Outlook: Recovery on the Horizon
Looking ahead, the Sweden economy 2025 outlook forecasts 0.9% to 1.6% GDP growth, per government and OECD5 estimates. Real wages rise and fiscal easing will fuel this, though US tariffs pose risks.
In Sweden economy news today 2025, optimism grows around labor market picks-up, with employment edging higher. Yet, global tensions could cap gains at 2.3% in 2026. Compared to Germany’s economy, Sweden’s smaller scale allows nimbler pivots to green tech.
Navigating Sweden Economy Problems in 2025
No outlook ignores hurdles. Sweden economy problems center on early-2025 recession signals, with GDP dipping amid tariff threats. Unemployment lingers high at 8.3%, outpacing EU averages, straining welfare systems.
Productivity slowdowns since the financial crisis add friction, per IMF6 notes. Yet, solutions abound: Boost R&D in AI and renewables to counter these. For parallels, check US economy challenges.
Finland vs Sweden Economy: A Nordic Rivalry
The Finland vs Sweden economy7 debate heats up in 2025. Sweden’s $610 billion GDP dwarfs Finland’s $300 billion, with per capita at $57,723 versus $53,286. Sweden leads in exports (cars vs. Finland’s tech), but both face labor woes—Sweden’s unemployment at 8.3% edges Finland’s 7.5%.
Sweden’s edge stems from diversified sectors, per world economy ranking.
Sweden Economy Sectors: Engines of Growth
Sweden economy sectors shine in services (70% of GDP), manufacturing (20%), and agriculture (2%). Standouts include telecom (Ericsson), pharma, and autos. In 2025, green steel and mining surge, with silver production aiding batteries. This mix drives the Sweden economy news September 2025 narrative of sustainability.
- Services: Banking and tourism rebound post-pandemic.
- Industry: Exports machinery to China’s market.
- Tech: R&D investments hit 3.5% of GDP.
What Type of Economy Does Sweden Have?
The Sweden economy thrives as a mixed economy, blending free-market drive with government oversight. Private firms innovate, while welfare ensures equity—think universal healthcare funded by taxes.
What type of economy does Sweden have? A mixed economy where capitalism meets socialism, fostering high trust and low inequality. Is Sweden a mixed economy? Absolutely; regulations curb excesses, unlike pure capitalism. What kind of economy is Sweden? Export-led and open, ranking high in competitiveness. Why is Sweden a mixed economy? It balances growth with social goals, avoiding command-style controls. Is Sweden a capitalist economy? Yes, with strong private ownership, but not unchecked.
This setup explains its stability, even in Sweden economy recession 2025 talks. How is the economy in Sweden? Resilient, with what is the economy like in Sweden marked by innovation hubs like Stockholm.
FAQs
What type of economy does Sweden have?
Sweden runs a mixed economy, mixing private enterprise with public welfare. This setup drives exports while protecting workers through strong unions and benefits. It ranks among Europe’s most competitive.
What kind of economy does Sweden have?
It’s a high-tech, export-focused mixed system. Businesses like IKEA thrive freely, but government taxes fund education and healthcare, keeping inequality low.
Is Sweden a mixed economy?
Yes, Sweden exemplifies a mixed economy. Free markets handle most production, but state intervention ensures fair wages and environmental rules, boosting long-term stability.
What economy is Sweden?
Sweden’s economy is advanced and open, with services and manufacturing leading. In 2025, it eyes 1% growth amid global trade shifts.
How is Sweden economy performing in 2025?
The Sweden economy shows slow recovery, with unemployment easing but tariffs looming. Positive wage hikes offer hope for a stronger 2026.
What is Sweden economy facing today?
Currently Sweden economy challenges include inflation and labor shortages. Yet, green investments and policy cuts provide a safety net.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for the Sweden Economy
Wrapping up, the Sweden economy navigates 2025 with measured steps—modest growth, trade surpluses, and sector strengths offsetting debts and uncertainties. From Sweden economy news today recency 3 to outlook projections, resilience defines it as a mixed economy model. As tariffs test exports, innovation in green tech and pharma will be key.
What aspect of the Sweden economy intrigues you most—its trade secrets or recession strategies? Share below!
References
- Wikipedia. (2025). Economy of Sweden. Retrieved from Wikipedia. (Overview; general readers.) ↩︎
- Swedish Geological Survey. (2025). Statistics of the Swedish Mining Industry 2024. Retrieved from SGU Report. (For silver production; audience: Researchers tracking mineral trends.) ↩︎
- Observatory of Economic Complexity. (2025). Sweden Exports, Imports, and Trade Partners. Retrieved from OEC World. (Trade data; for business analysts.) ↩︎
- Reuters. (2025, Oct 23). What France and others can learn from Sweden’s hard budget lessons. Retrieved from Reuters. (Fiscal news; policymakers.) ↩︎
- OECD. (2025). Economic Surveys: Sweden 2025. Retrieved from OECD. (Outlook; economists.) ↩︎
- IMF. (2025, Apr 1). Sweden: Selected Issues. Retrieved from IMF. (Productivity; academics.) ↩︎
- CountryEconomy.com. (2025). Country comparison Sweden vs Finland. Retrieved from CountryEconomy. (Comparisons; comparative studies.) ↩︎